Ice viscous anisotropy
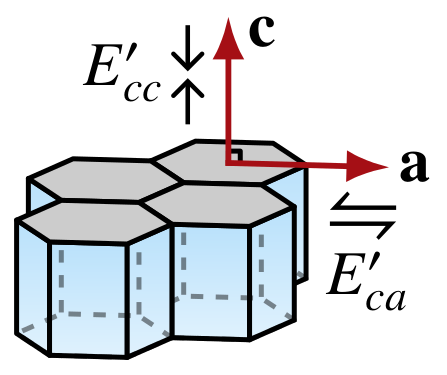
If ice grains are treated as transversely isotropic, the rheology of a single grain can be modeled as a transversely isotropic power law. This requires specifying the grain eigenenhancements \(E_{cc}'\) and \(E_{ca}'\) and the power law exponent \(n'\).
The grain parameters proposed by Rathmann and Lilien (2021) assume linear-viscous behavior of single crystals (\(n'=1\)) and promote the activation of basal glide by making that slip system soft compared to other systems: \(E_{ca}' > 1\), whereas \(E_{cc}'=1\). This reduces the problem to picking \(E_{ca}'\) and \(\alpha\) (Taylor—Sachs homogenization weight), which Rathmann and Lilien (2021) determined by requiring that deformation tests on strong single-maximum CPOs (aligned grains) are approximately reproduced; that is, \(E_{mt}=10\) and \(E_{mm}=0.01\).
The effect of choosing different \(E_{ca}'\) and \(\alpha\) (left panel) on the eigenenhancements of different CPO states (right panel) is shown below for combinations of \(E_{ca}'\) and \(\alpha\) that fulfill \(E_{mt}=10\) given a unidirectional CPO.
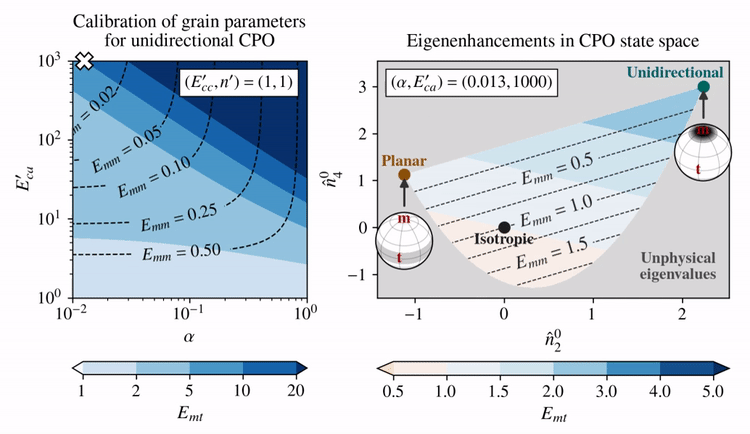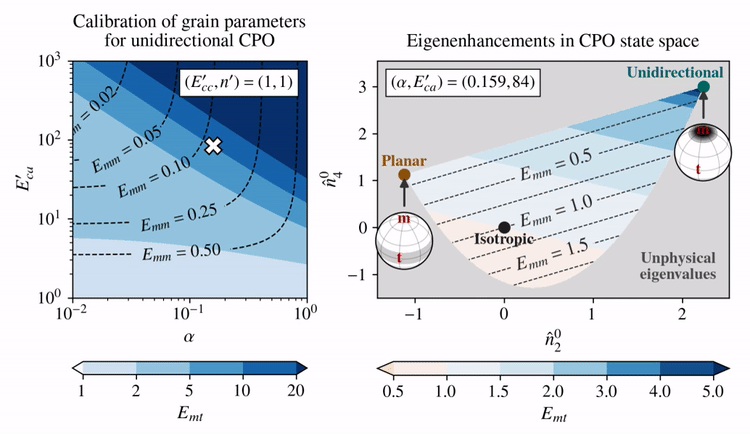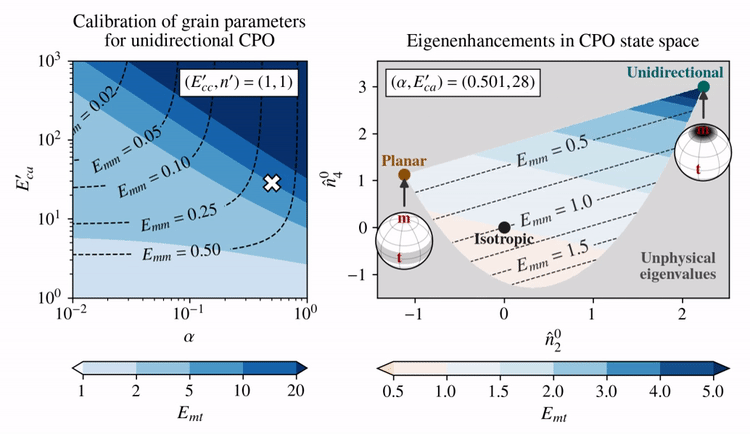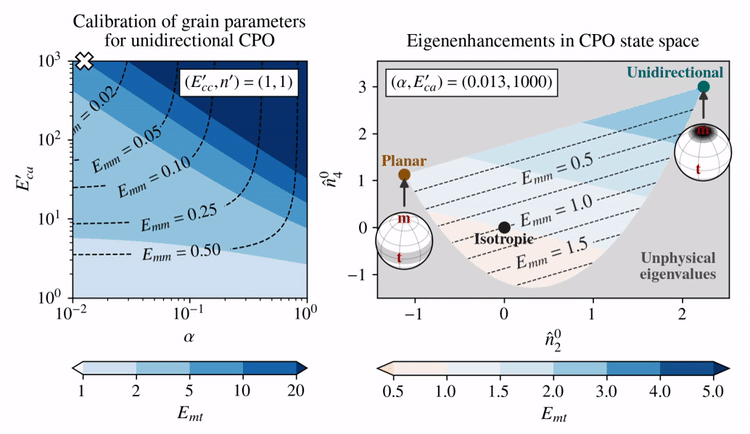
Clearly, there is a trade-off between how shear enhanced (\(E_{mt}\)) and how hard for axial compression (\(E_{mm}\)) the model allows a unidirectional CPO to be.
📝 Code example
The below code shows how to calculate \(E_{ij}\) given \({\bf a}^{(4)}\) (or the state vector \(\bf s\)) and a set of grain parameters.
import numpy as np
from specfabpy import specfab as sf
lm, nlm_len = sf.init(8)
### Synthetic unidirectional CPO (all c-axes aligned in z-direction)
m = np.array([0,0,1])
a4 = np.einsum('i,j,k,l', m,m,m,m) # fourth-order structure tensor
nlm = np.zeros((nlm_len), dtype=np.complex64)
nlm[:sf.L4len] = sf.a4_to_nlm(a4) # corresponding expansion coefficients
### Enhancement factor basis
ei, lami = sf.eig(nlm) # use a^(2) basis (m1,m2,m3; i.e. eigenenhancements)
#ei = np.eye(3) # use Cartesian basis (x,y,z)
### Transversely isotropic monocrystal parameters for ice (Rathmann & Lilien, 2021)
n_grain = 1 # power-law exponent: n_grain=1 => linear grain rheology, nonlinear (n_grain>1) is unsupported.
Eij_grain = (1, 1e3) # grain eigenenhancements for compression along c-axis (Ecc) and for shear parallel to basal plane (Eca)
alpha = 0.0125 # Taylor--Sachs weight
### Calculate enhancement factors in ei frame
Eij = sf.Eij_tranisotropic(nlm, *ei, Eij_grain,alpha,n_grain) # Eij=(E11,E22,E33,E23,E13,E12)